This blog is for ITC 493 assignment
Monday, October 29, 2007
Planning of this blog's 'afterlife'
First, I will use this blog site as a notebook. I want to save some good articles about IT project management in it, or write some my own experiences, ideas, or lessons about IT project management. My blog is open, anyone can read it. I like to share it with other friends.
Second, my blog site could be a small forum. Sometimes, I could paste some questions or cases on it, and discuss them with other friends. They could write comments to express their opinions. They could provide questions and cases as well.
Blog site is a good platform for communication, expression, discussion, and share information. I believe my little blog site will have a quite long “life”.
ITC 493 Assignment 2 Task 2 Chapter 11
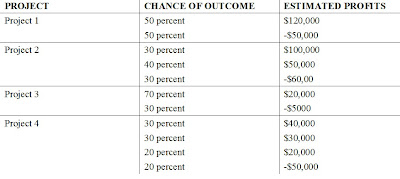
A: Please click the picture or open the picture in the new window to display the whole Expected Monetary Value (EMV) diagram.
Please click the link to download the source file.
http://www.box.net/shared/6nuvj8nxqj
The EMV for Project 1 is:
0.5×120000 + 0.5× (-50000) = 60000 - 25000 = $35000
The EMV for Project 2 is:
0.3×100000 + 0.4×50000 + 0.3× (-60000) = 30000 + 20000 – 18000 = $32000
The EMV for Project 3 is:
0.7×20000+0.3×(-5000) = 14000 – 1500 = $12500
The EMV for Project 4 is:
0.3×40000+0.3×30000+0.2×20000+0.2×(-50000)= 12000 + 9000 + 4000 – 10000 = $15000
As Schwalbe (2006, p.449) indicated, “Because the EMV provides an estimate for the total dollar value of a decision, you want to have a positive number; the higher the EMV, the better.” In terms of this, I evaluate each project’s EMV first. All projects’ EMVs are positive, it’s great. But I want the highest profit, so I choose the project which has the highest EMV to bid on. The EMV for Project 1 is the highest ($ 35,000). Accordingly, I would bid on the project 1.
To be a good project manager, I should try to balance the risk and profit, which means I will try to find the best balance point (in my opinion) between the risk and profit. From the EMV diagram, we could find:
For project 1, we have 50 percent chance to earn $120,000, and 50 percent chance to lost $50,000;
For project 2, we have 30 percent chance to earn $100,000, 40 percent chance to earn $ 50,000, and 30 percent chance to lost $ 60,000;
For project 3, we have 70 percent chance to earn $20,000, 30 percent chance to lost $ 5,000;
For project 4, we have 30 percent chance to earn $40,000, 30 percent chance to earn $30,000, 20 percent chance to earn $20,000, and 20 percent chance to lose $ 50,000.
If we just looked the potential outcome of these projects, project 1 is the best, since we could earn $120,000 (50 percent chance) from it. If we just looked the potential risk of these projects, project 3 is the best, since we maybe only lost $5,000 (30 percent chance). However, I would like to bear the risk and pursue the biggest profit. The risk of project 1 is positive risk which could give us plentiful repayment. Therefore, I still would choose the project 1 to bid on.
Normally, just as Schwalbe (2006, p.449) said, “Using EMV helps account for all possible outcomes and their probabilities of occurrence, thereby reducing the tendency to pursue overly aggressive or conservative risk strategies.” A good project manager should consider both of EMV information and personal risk tolerance to make the decision.
Reference
Schwalbe, Kathy, 2006, “Information technology project management 4th”, Thomson Course Technology, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Sunday, October 28, 2007
ITC 493 Assignment 2 Task 2 Chapter 10
a. Many of the technical staff on the project come in from 9:30 to 10:00 a.m. while the business users always come in before 9:00 a.m. The business users have been making comments. The project manager wants to have the technical people come in by 9:00, although many of them leave late.
b. Your company is bidding on a project for the entertainment industry. You know that you need new ideas on how to put together the proposal and communicate your approach in a way that will impress the customer.
c. Your business has been growing successfully, but you are becoming inundated with phone calls and e-mails asking similar types of questions.
d. You need to make a general announcement to a large group of people and want to make sure they get the information.
A:
For scenario “a”, if the technical people could arrive on time, meeting is the best media for this scenario’s communication, because the technical people could discuss the project with the business users face to face, and both of them could understand each other easily. The technical people could make response to users’ questions immediately. And the technical people also could understand users’ requirements better. This is good for developing the project. Therefore, the project manager should try his/her best to ask the technical people arrive on time.
But if the technical people could not arrive on time, then we choose phone call as another communication media. Although it is not as good as meeting, it is still useful for technical people and the business users to exchange information. When business users come, the project manager should answer their questions to the best of his/her ability. If the project manager couldn’t answer the questions, then he/she records users’ questions and requirements. When the technical people arrive, ask them ring users to answer their questions, or in terms of users’ requirements to change the system.
For scenario “b”, meeting is the most appropriate media to use. Now, I need some new ideas, or some suggestions. Brainstorm is the best way to get them. It means these ideas or suggestions should come from many people. Therefore, meeting is the most appropriate media.
For scenario “c”, web site is the most appropriate media to use. Since these phone calls and e-mails asking similar types of questions, then their answers should be similar. Using web site to publish these familiar questions’ answers, and asking users or customers to look through the web site to find their questions’ answers, it will reduce my energy and time.
For scenario “d”, e-mail is the most appropriate media to use. Since I only make a general announcement and will give it to a large group of people, e-mail is the easiest way to do it. I can send group e-mails to many people, and use e-mail receipts to make sure all people get the information.
Friday, October 26, 2007
ITC 493 Assignment 2 Task 2 Chapter 9
A: Please click the picture or open the picture in the new window to display the whole image.
Please click the link to download the source file. http://www.box.net/shared/th17pkao0t
Thursday, October 25, 2007
ITC 493 Assignment 2 Task 2 Chapter 8
A:
Professional Background:
1. Candidate’s degree
The candidate should have Master or higher degree of Computer Science, Information Technology or related area.
2. Work experience
The candidate should have several years work experiences in the project manager position. It is better if the candidate has work experiences in the big company.
3. Teaching experience
The candidate should have taught the project management course before.
Personality:
1. The candidate should have passion in teaching.
2. The candidate should be patient to students.
3. The candidate should have good communication skill.
4. The candidate should have good oral expression ability.
5. The candidate should be positive.
Others:
1. The candidate should be health.
2. The candidate’s salary requirement should reasonable (within our budget).
3. The candidate should have free time to meet the course timetable.
4. The candidate could teach this course for a long period.
5. Look the candidate whether has some special requirements (single office, teach assistant, etc.).
Q2: Create a Pareto diagram based on the information in the table below. First, create a spreadsheet in Excel, using the data in the table below. List the most frequent cstomer problems first. Add a column called "% of Total" and another one called "Cumulative %." Then enter formulas to calculate those items. Next, use the Excel Chart Wizard to create a Pareto diagram based on this data. Use the Line - Column on 2 Axis custom type chart so your resulting chart looks similar to the one in Figure 8 -1. (Chapter 8, Exercise 2, page 330)
A: Please click the picture or open the picture in the new window to display the whole image.
Please click the link to download the source file. http://www.box.net/shared/1u4hm9s2ds
Sunday, September 16, 2007
ITC493 Assignment 1 Task 2 Chapter 6
A: Please click the picture or open these pictures in the new windows to display the whole images.

Figure 1. Gantt chart

Figure 2. Network diagram

Figure 3. Schedule
The network diagram (Figure 2) which I created in this exercise is as Figure 6-4 in the text book.
Schwalbe (2006, p.220) indicated, “Since the critical path is the longest path through the network diagram……” Then we could find the critical path for Project X from the network diagram. When we know the critical path, we could make clear which activities determine the earliest completion of the project X. It means when we make schedule, we should pay attention to those critical activities to shorten the schedule. We could allocate more resources to those activities to shorten the project schedule. We also could reduce some critical activities’ duration to shorten the project schedule.
From the schedule table, we could easily find early and late start and finish dates and free and total slack amounts for activities. When we know the number of float or slack, we could determine whether this schedule is flexible and its flexible grade. Then we could use this as the basis to negotiate the project schedule.
So both of network diagram and schedule table are useful tools to help set down and adjust the Project X's schedule.
Reference
Schwalbe, Kathy, 2006, “Information technology project management 4th”, Thomson Course Technology, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Please click the link to download the source file
http://www.box.net/shared/fun40upf3l
Saturday, September 15, 2007
ITC493 Assignment 1 Task 2 Chapter 5
A: Please click the picture or open the picture in the new window to display the whole image.

Please click the link to download the source file
http://www.box.net/shared/uch7ah9pvp
Q6: Create the same WBS described in Exercise 1 using Project 2003, indenting categories appropriately. Use the outline numbering feature Options, and then click Show outline number). For example, your WBS should start with 1.0 Initiating. Do not enter any durations or dependencies. See Appendix A or Project 2003’s Help for assistance. Print the resulting Gantt chart on one page, being sure to display the entire Task Name column. (Chapter 5, Exercise 2, page 195)
A: Please click the picture or open these pictures in the new windows to display the whole images.


Please click the link to download the source file
http://www.box.net/shared/5xun7gjyxq
http://www.box.net/shared/h3ke3x3vml
Tuesday, September 11, 2007
ITC493 Assignment 1 Task 2 Chapter 4
A: Please click the picture or open these pictures in the new windows to display the whole images.
.jpg)
Figure 4-2
.jpg)
Figure 4-3
.jpg)
Figure 4-4
.jpg)
Figure 4-5
Please click the link to download the source file
http://www.box.net/shared/jq5fgsktcm
Thursday, September 6, 2007
ITC493 Assignment 1 Task 2 Chapter 3
A: This Gantt chart is based on Figure 3-2 (page 95) in the text. (Please click the picture or open this picture in the new window to display the whole image. )

please click the link to download the source file
http://www.box.net/shared/i6ydv1dgzz
Saturday, August 25, 2007
ITC493 Assignment 1 Task 2 Chapter 2
A:
Almost all key stakeholders or sponsors in information technology projects are in top management positions. And if the project manager could gain enough top management support, the success rate of this project will be high. Therefore top management support is one of important factors of project success.
In the project development process, there will be many changes. Some of them will be controlled by project manager, but unfortunately some of them will out of control. Then the project manager will need stakeholders’ or sponsors’ help. So actually, top management support will be necessary when changes come. Schwable (2006, p.51) indicated some reasons that why top management support is very important to project managers:
1. Project managers need adequate resources.
2. Project managers often require approval for unique project needs in a timely manner.
3. Project managers must have cooperation from people in other parts of the organization.
4. Project managers often need someone to mentor and coach them to leadership issues.
As Goldenberg (2001) said, “True support is not about getting a signature on the check. That's one key point, but it's not enough. Sponsors need to round up the troops, get the word out that the project is important to the company and protect people when difficulty happens.”
So, when the project managers need sufficient resources such as money, human resources and other materials for the project, with top management support, they could get what they need easily, and then it won’t influence the project development. Top management should understand that the project development is uncertain, changes cannot be avoided. In different time, the develop team will have different specific needs for the project, top management should meet them. Nowadays, many information technology projects are across different functional areas. Therefore, project managers sometimes will need cooperation from other departments. Top management should help project managers to deal with this. Top management also should teach new project managers who just come from technical positions how to be good managers and leaders. Top management should pass on their experiences to new project managers.
In conclusion, although with top management support doesn’t mean the project will succeed, but without top management support the project will fail.
Reference
Schwalbe, Kathy, 2006, “Information technology project management 4th”, Thomson Course Technology, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Goldenberg, Barton, “Getting and Keeping Top Management Support”, CRM Magazine November 2001, http://www.destinationcrm.com/articles/default.asp?ArticleID=1219, 08/25/2007
Wednesday, August 22, 2007
ITC493 Assignment 1 Task 2 Chapter 1
A:
The CHAOS Report (1994) is an article about failure factor and success factor of information technology project.
In this article, at first, software development is compared with bridge building. The failure of software development is more than bridge building’s. One of the biggest reasons is the design of a bridge is more certain than software’s. When a bridge’s design and contract have been confirmed, they normally won’t be changed. But it seems impossible for IT projects. Nowadays, the business environment is ever changing. It is difficult to keep the requirement of a project unchangeable. Just this uncertainty makes many information technology projects fail. Unfortunately, not like bridge building, many computer companies don’t learn lessons from the failure. Therefore we still make the same mistakes again and again.
Secondly, this article provides some statistics about failures of projects. In 1994, about $250 billion were spent on 175,000 IT projects in the United States. The average only 16.2% of these projects were completed on-time and on-budget. Almost 31.1% of projects were canceled before they ever got completed. Almost 52.7% of projects cost 189% of their original budget. Even in those completed projects, a good few didn’t match the original specification requirements. And quite a few projects got delayed. Large companies’ situations are worse than medium companies’ and small companies’. The main reason of cost and time overruns is restart. Almost 94% of projects will restart and not only once.
Thirdly, this article discusses success and failure reasons of IT projects. The three major success reasons are user involvement, executive management support, and a clear statement of requirements. The top two failure causes are incomplete requirements and lack of user involvement. For further insight into failure and success, The Standish Group focused on four groups with IT executives of major companies- California DMV, American Airlines, Hyatt Hotels, and Banco Itamarati. Because of incomplete statement of requirements, lack of user involvement, and poor requirements and specifications, the former two companies’ projects failed. Whereas, the latter two companies, they had user involvement, a clear statement of requirements, executive management support, and proper planning, therefore their projects succeed.
At last, The Standish Group indicates that if deliver software components early and often in smaller time frames, it will increase the success rate. Shorter time frames bring on a repeated process of design, prototype develops, test, and deploy small elements. This process is known as “growing” software. It will make users earlier engaged, every component has its own owner, and expectations are realistically set. Every component has clear and accurate statements and aims. This could make projects simpler, and reduce confusion and cost.
In conclusion, I think, with the project is bigger, the difficulty of its management is bigger. So this is why the situation of large company is worse than medium company and small company. To make one project success, we should let the user join our development team. It means we should survey the sponsor, the user, everyone who will use this system. Let them tell us what they really want, what they really need. Only after that, we could write a clear and accurate system requirement. It is very important to make a clear and accurate requirement for project. It will influence this project whether will be restarted and succeed. Spending some time on this will reduce the project’s time in future. And we should all along keep touch with the user, if they need change, we could make responses immediately. At the same time, we could get their technology supports and feedback as well. Project managers should make a proper planning. It means they should assort with scope, time, and cost. Then mangers make a good schedule which will insure the project succeeds. Project managers should know how to decompose a large, complex, difficult system into small, simple, easy sub-systems. Making difficult problem easy will improve project success rate.
Reference
The CHAOS Report (1994), Standish Group, http://www.standishgroup.com/sample_research/chaos_1994_1.php, 8/22/07